The Russia-Ukraine war began on February 24, 2022, as explosions echoed across Ukrainian cities and Russian forces crossed the border. The invasion was not a sudden event but the result of years of rising tensions between the two nations. It was a war born out of clashing visions for Ukraine’s future—one seeking independence and alignment with the West, and the other tied to Moscow’s efforts to maintain its influence over the region.
For Russia, Ukraine held deep historical and strategic significance. Moscow viewed Ukraine’s growing ties with NATO and the European Union as a threat to its security. For Ukraine, this conflict was not just about defending its land but about protecting its right to choose its path as a sovereign nation. The war became a struggle for identity and freedom, with the people of Ukraine refusing to back down despite overwhelming odds.
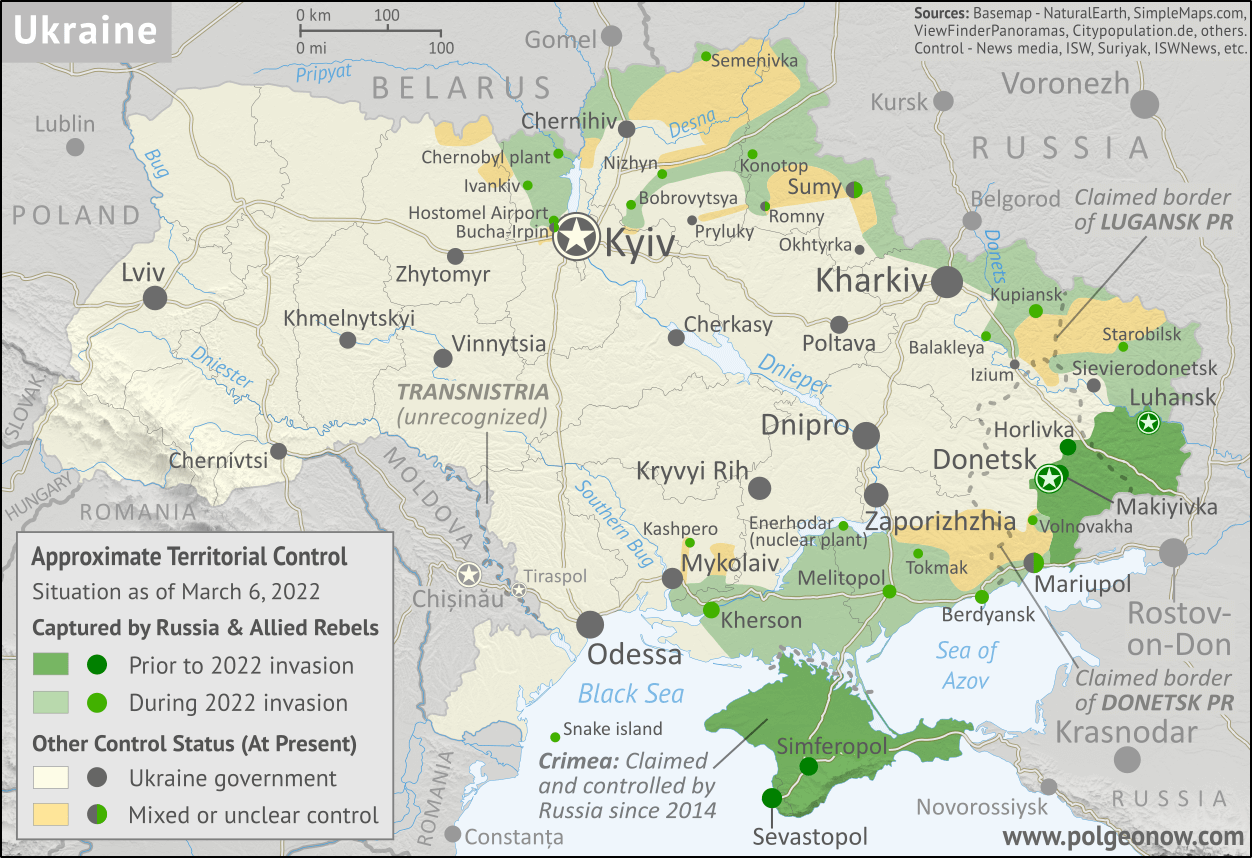
Phase 1: Initial Invasion and Rapid Escalation (February–May 2022)
On February 24, 2022, the simmering tensions erupted into a full-scale invasion. In what Russian leaders labeled a campaign to “denazify” Ukraine, airstrikes rained down on cities like Kyiv, Kharkiv, Mariupol, and Odessa, thrusting the nation into chaos.
The invasion’s initial days saw a dramatic escalation in hostilities. Russian forces aimed for a swift victory, targeting Ukraine’s leadership and critical infrastructure. However, Ukraine’s response, led by President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, defied expectations. Ukrainians, from soldiers to civilians, rallied with extraordinary resilience, repelling Russian advances into Kyiv. This phase of the war highlighted not just the might of modern warfare but also the indomitable spirit of a people fighting for their homeland.
The cost of war extended far beyond the battlefield. Over 13 million people—nearly one-third of Ukraine’s pre-war population—were displaced. Of these, more than 8 million sought refuge abroad, marking Europe’s largest refugee crisis since World War II. In besieged cities like Mariupol, where Russian shelling was relentless, the civilian toll became a grim symbol of the war’s human cost. Blockades and airstrikes created catastrophic conditions, depriving millions of electricity, clean water, and medical care. Hospitals, schools, and residential areas bore the brunt of attacks, leaving Ukraine’s already fragile infrastructure in ruins.
The Mariupol siege encapsulated this humanitarian crisis. Thousands perished in airstrikes, while survivors endured starvation and disease in shelters cut off from aid. Meanwhile, Russia’s alleged forcible transfer of up to 1.6 million Ukrainians, including children, to its territories added another layer of tragedy. The international community condemned these actions, citing potential war crimes, but the suffering on the ground continued unabated.
This early phase of the war set the tone for what followed: a protracted conflict marked by resilience, devastation, and the struggle for sovereignty in the face of overwhelming aggression
Phase 2: Consolidation and Regional Focus (June–December 2022)
After the fierce resistance of the early months, Russia shifted its strategy, withdrawing from northern Ukraine, including Kyiv, and focusing on the eastern Donbas region. This marked the beginning of a grinding phase of the war, defined by intense battles over key cities like Severodonetsk and Lysychansk. By mid-2022, Russian forces had captured these cities, giving them control over large parts of Luhansk oblast. However, Ukraine’s determination remained unbroken, setting the stage for a prolonged struggle.
The Atrocities in Bucha and Irpin
As Russian forces retreated from northern areas, the world witnessed the grim aftermath of their occupation. In towns like Bucha and Irpin, evidence of widespread war crimes emerged, with hundreds of civilian bodies discovered, many showing signs of torture and execution. Mass graves, including one behind a local church in Bucha, became symbols of the war’s brutality. Survivors described living through atrocities, reinforcing calls for justice and accountability for these acts
The Role of Sanctions and Western Support
The international response escalated during this period. Western nations, led by the United States and the European Union, imposed severe economic sanctions targeting Russia’s economy. At the same time, they ramped up military aid to Ukraine, including the provision of advanced weapons like the HIMARS rocket systems. These long-range precision weapons allowed Ukraine to strike deep into Russian-controlled territory, disrupting supply lines and weakening Moscow’s offensive capabilities
Ukraine’s Defiance and the World’s Solidarity
Despite immense challenges, Ukraine’s resilience continued to inspire global solidarity. President Zelenskyy’s leadership galvanized international support, ensuring a steady flow of humanitarian aid and military resources. This period underscored the evolving nature of the war—from a rapid invasion to a protracted and deeply destructive conflict—while highlighting the stark contrast between the aggressor’s tactics and Ukraine’s struggle for survival and sovereignty.
This chapter of the war highlighted both the human cost and the geopolitical stakes, as Ukraine fought not just for its land but for the very principles of freedom and independence, drawing an unwavering line against aggression.
Phase 3: Counteroffensive and Momentum Shift (2023)
Reclaiming Ground Amid Resilience
By the spring of 2023, the tides of the conflict began to shift as Ukraine launched counteroffensives that reclaimed territories and shook Russian military confidence. One of the defining moments was the recapture of Kherson in late 2022, a victory achieved despite Russia’s fortified defenses and strategic flooding of areas near the Dnipro River. Ukrainian forces then advanced in the Kharkiv and Donetsk regions, reclaiming towns such as Izyum and Lyman. These successes were attributed to a mix of Ukrainian tactical planning, effective use of HIMARS artillery systems, and months of U.S. and NATO training that elevated the Ukrainian military’s capabilities to match Russian forces in precision and coordination
These victories also demonstrated the growing role of intelligence in modern warfare. Ukraine’s military misled Russia into reinforcing southern fronts near Kherson while launching surprise operations in the northeast. This operational manoeuvring allowed Ukrainian forces to punch through weakly defended areas, capturing key supply hubs and breaking Russian defensive lines
Growing Geopolitical Tensions
Ukraine’s battlefield achievements coincided with major shifts in global geopolitics. NATO expanded, with Finland officially joining in April 2023, signalling a stark rebuke to Moscow’s aggression. Sweden’s NATO membership advanced, further tightening the alliance’s eastern flank. At the same time, Western nations doubled down on support for Ukraine, committing billions in military aid, including tanks, advanced missile systems, and training. This support underscored a unified message: the international community would not tolerate territorial revisionism through force
Russia’s Energy Gambit
Amid battlefield losses, Russia escalated its strategy of economic warfare, weaponizing energy supplies to Europe. Gas supplies were curtailed, leading to an energy crisis across the continent. However, European nations adapted by diversifying energy imports and accelerating renewable energy projects, reducing their dependence on Russian energy. Meanwhile, Ukraine continued to operate its energy infrastructure under perilous conditions, displaying resilience in the face of targeted Russian strikes on its power grids
This phase of the war reflected a critical shift, as Ukraine moved from defensive survival to active reclamation of its sovereignty, while the global order rallied against the aggression. The victories on the battlefield, coupled with international unity, marked a turning point in Ukraine’s fight for independence and democratic values.
Phase 4: Prolonged Stalemate and Evolving Strategies (2024)
The transition to 2024 brought a new chapter of the war, characterized by entrenched battles and strategic recalibrations. Intense fighting in the Donbas region, particularly in Bakhmut, underscored the conflict’s grueling nature. Russian missile strikes targeted Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, plunging millions into winter blackouts. Meanwhile, drone warfare became pivotal. Both sides employed drones extensively for reconnaissance and strikes, with Ukraine using advanced long-range drones to target Russian military and energy facilities deep inside its territory, including attacks on critical oil infrastructure.
The humanitarian toll deepened as the war’s devastation spread. By mid-2024, over 11,700 civilian deaths were recorded, with millions displaced. Essential services like electricity and healthcare were severely disrupted, and schools and hospitals came under frequent attack. The UN and humanitarian organizations intensified efforts to address these crises, appealing for $3.1 billion in aid to support the 8.5 million most vulnerable people in Ukraine. Yet, the challenges of displacement, disrupted infrastructure, and psychological trauma persisted
This phase emphasized the evolving nature of modern warfare, with technology playing a crucial role. While Ukraine’s counteroffensive showcased its growing military proficiency and international backing, the prolonged stalemate highlighted the enduring costs and complexities of reclaiming sovereignty in a conflict that has reshaped global geopolitics.
Recent Developments (July–November 2024)
Escalating Offensives
As the war entered late 2024, Russia intensified its attacks, launching one of the largest waves of missile strikes in months, targeting major Ukrainian cities such as Kyiv and Odessa. These strikes caused significant destruction to civilian infrastructure and further displaced families. Ukrainian forces, in response, continued their counterattacks, striking key Russian military positions in occupied territories and even across the Russian border. The use of drones became increasingly prominent, with both sides deploying them for reconnaissance and targeted attacks
One of the most tragic incidents during this period was the missile strike on Okhmatdyt, Ukraine’s largest children’s hospital in Kyiv, on July 8, which killed two and injured over a hundred, including children. This attack, alongside others on civilian facilities, reignited international condemnation and calls for justice
Geopolitical Dynamics
On the global stage, geopolitical tensions continued to evolve. U.S. President-elect Donald Trump signaled potential policy changes, sparking diplomatic recalibrations among Russia, Ukraine, and their allies. Meanwhile, international bodies intensified their efforts to hold Russia accountable for war crimes, including forced deportations, torture, and targeting of civilian infrastructure. Investigations into these atrocities gained momentum, with tribunals expected to bring perpetrators to justice.
Impact and Outlook
The humanitarian crisis deepened, with over 11,700 civilian deaths reported and millions displaced. Ukraine’s economy and infrastructure faced severe devastation, while global food and energy markets remained under strain due to the conflict. As both sides braced for a prolonged winter of hostilities, the war’s future trajectory remained uncertain. Peace appeared elusive, with the conflict continuing to reshape international alliances and global power balances

